GA4 vs. Universal Analytics: What You Need to Know

Written by: EasyAutoTagging Staff Read time 10 minutes
In the world of digital marketing, Google Analytics is an essential tool that provides businesses with the data they need to optimize their digital strategy. When we talk about UA and GA4, we are referring to two different versions of Google Analytics. UA stands for Universal Analytics, and GA4 stands for Google Analytics 4. The most significant difference between these two versions is the way they organize and process data. According to the latest stats, UA is still more widely used than GA4, with a market share of 84.4% compared to GA4’s 15.6%.
Both Universal Analytics and GA4 serve the purpose of tracking website and app performance, but they have significant differences. As forced migrations are set to begin in March 2023 and Universal Analytics is set to be sunset by the end of June 2023, it is crucial to understand the key distinctions between the two. This blog post will examine 10 differences between Universal Analytics and GA4 to help you prepare for the transition.
1. The GA4 Event Based Data Model:
The most significant difference between UA and GA4 is their data model. UA uses a session-based model, while GA4 uses an event-based model. In UA, a session is a set of interactions a user has with a website or app within a specific time frame. In GA4, an event is any action that a user takes on a website or app.
In Universal Analytics (UA), data is organized around sessions. A session is essentially a collection of interactions that a user has with a website or app within a specific time period. These interactions could include things like pageviews, clicks, and other actions that the user takes during their visit. UA groups all of these interactions together and treats them as a single session.
On the other hand, in Google Analytics 4 (GA4), data is organized around events. An event is any action that a user takes on a website or app. This could include things like pageviews, clicks, form submissions, and other actions. GA4 tracks each of these actions as a separate event and allows you to analyze them individually.
With GA4’s event-based model, you have more granular data and can track specific actions more accurately. However, you may need to do some extra work to group events together if you want to analyze them as a session.
2. Anonymized Cross-Device Tracking:
Cross-device tracking is a method of tracking user activity across multiple devices, such as a user browsing on their phone and then later on their laptop. This allows website and app owners to gain a more complete understanding of their users’ behavior and preferences.
In UA, the User-ID feature is used for cross-device tracking. This feature requires users to log in to your website or app in order to track their activity across devices. Once a user has logged in, they are assigned a unique User-ID that is used to track their activity across all devices where they are logged in.
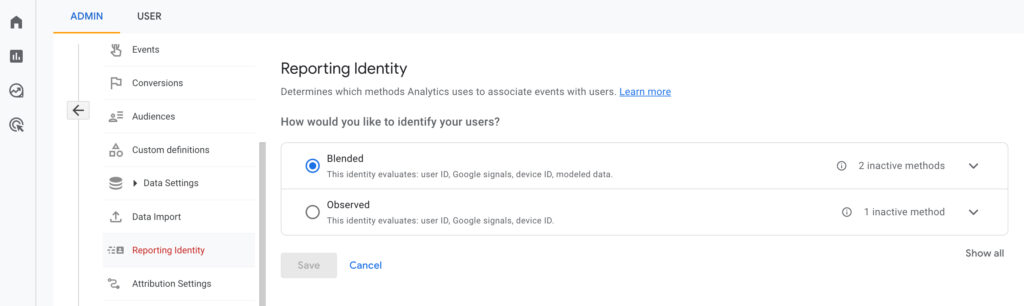
On the other hand, GA4 uses the Cross-Device ID feature for cross-device tracking. This feature is different from User-ID because it does not require users to log in to your website or app. Instead, GA4 uses an anonymous identifier, called the Cross-Device ID, to track user activity across devices.
The Cross-Device ID is created using machine learning algorithms and statistical modeling to determine which devices are likely to belong to the same user. It is an anonymous identifier that does not reveal the user’s identity, but rather allows Google to track their activity across devices.
So, in summary, User-ID and Cross-Device ID are both features used for cross-device tracking, but they work in slightly different ways. User-ID requires users to log in to your website or app, while Cross-Device ID is an anonymous identifier used by GA4 to track user activity across devices without requiring a login.
3. Improved Tracking Code:
In the past, the tracking code for GA was known as Universal Analytics (UA). However, with the introduction of a new version of GA called GA4, the tracking code has been updated to use the Global Site Tag (gtag.js).
Now, you might be wondering what the difference is between these two tracking codes. Well, one of the main advantages of gtag.js over UA is that it’s more streamlined and efficient. This means that it’s faster and uses less resources, which can improve the overall performance of your website.
So, if you’re using GA, it’s worth considering switching to gtag.js if you haven’t already. It’s a more modern and efficient tracking code that can help you get more insights into your website’s performance and improve your overall digital marketing efforts.
4. Cookie-Less Data Collection:
So, both UA and GA4 are tools used for web analytics, but they use different methods to track user activity. UA uses cookies, which are small text files stored on the user’s device, to track user behavior on a website. Cookies can capture basic information such as page views, session duration, and user demographics.
On the other hand, GA4 uses an event-driven model that collects data through JavaScript. This means that GA4 can track more complex user interactions beyond the basic information captured by cookies. For example, GA4 can track video plays, button clicks, form submissions, and scroll depth.
In essence, GA4 provides a more detailed and accurate analysis of user behavior compared to UA.
5. Leverage Machine Learning:
GA4 comes with some exciting features that are powered by machine learning, making it easier for businesses to get more valuable insights from their data.
One of these features is predictive analytics. Predictive analytics is a technique that uses statistical algorithms and machine learning models to analyze data and predict future outcomes. With GA4, businesses can use predictive analytics to identify trends and patterns in user behavior, such as which pages on their website are most popular and which marketing campaigns are most effective. This can help businesses make more informed decisions about their marketing strategies and improve their overall performance.
Another benefit of GA4 is that it provides a more complete view of the customer journey, from acquisition to retention. This is because it allows businesses to track user interactions across multiple devices and platforms, including mobile apps and websites. This can help businesses understand how users are engaging with their brand and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly.
6. Accessible Data Retention Settings:
With UA, users have the ability to choose their own data retention settings. This means that you can decide how long you want Google to keep your analytics data for. By default, Google will keep your data for 26 months, but you can adjust this setting to be shorter or longer, depending on your needs.
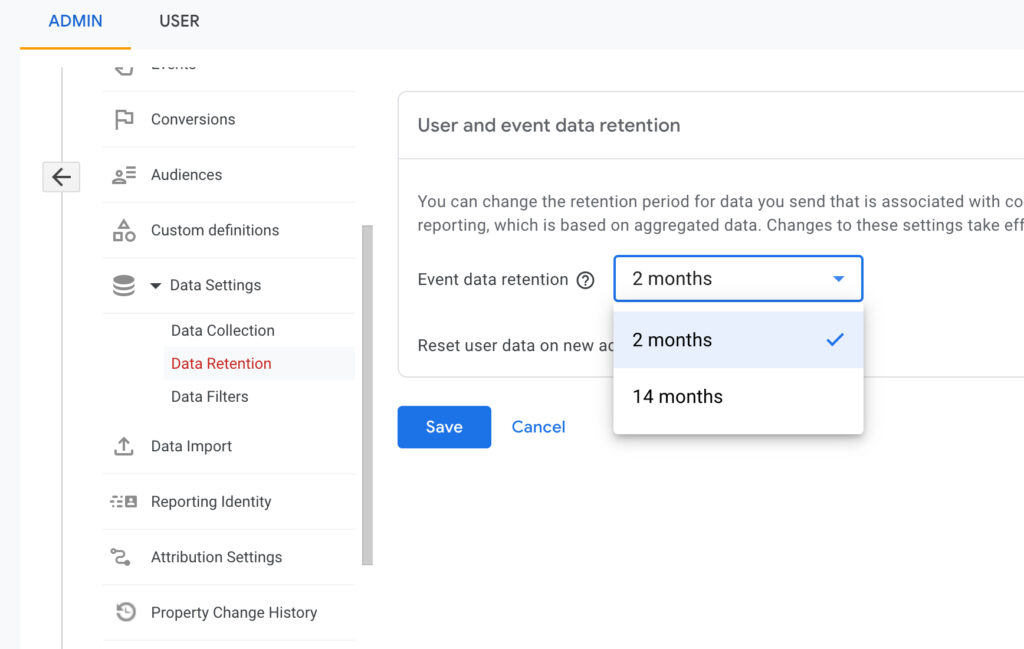
On the other hand, GA4 has a default retention period of 14 months. This means that Google will automatically delete your data after 14 months unless you adjust the retention period for specific data sets. For example, you might want to keep certain data for longer than 14 months, such as conversion data or user behavior data. In this case, you can adjust the retention period for those specific data sets to ensure that they are not deleted after 14 months.
Overall, both UA and GA4 give users some control over their data retention settings, but the default retention periods differ between the two tools. It’s important to understand how data retention works in order to make informed decisions about how to use these analytics tools effectively.
7. E-commerce Tracking in GA4:
First of all, GA4 makes it easier to track transactions across multiple currencies. It automatically converts currencies and displays revenue data in the currency of your choice. This feature is particularly useful if you operate in different countries with different currencies.
Secondly, GA4 provides more detailed and improved reporting. It allows you to track not just sales, but also other important e-commerce metrics such as add-to-cart, cart abandonment rate, and checkout abandonment rate. These metrics help you identify areas for improvement in your online store.
Finally, GA4 has more accurate revenue tracking than UA. It uses advanced machine learning algorithms to differentiate between refunds and cancellations, and it tracks revenue based on the actual payment amount received by the merchant. This ensures that your revenue data is as accurate as possible.
So, to sum it up, GA4 is a more advanced e-commerce tracking tool compared to UA. It supports multiple currencies, provides more detailed reporting, and has more accurate revenue tracking. Let me know if you have any more questions!
8. Get More Custom Dimensions and Metrics:
In Google Analytics Universal Analytics (UA), you can create up to 20 custom dimensions and metrics, which can be used to track additional data about your users and their behavior on your website or app. These custom dimensions and metrics can be used to capture information that is not included in the standard data that Google Analytics tracks, such as user roles, product categories, or customer lifetime value.
On the other hand, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) allows for up to 50 custom dimensions and 50 custom metrics, which provides even more flexibility in tracking and analyzing user behavior. This is particularly useful for businesses and websites that require more in-depth tracking and analysis capabilities, as it allows for a more granular view of user behavior and interactions.
Overall, the increased number of custom dimensions and metrics in GA4 can help businesses gain a better understanding of their users and make more informed decisions based on their data.
9. The GA4 Updated Reporting Interface:
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has a more streamlined and user-friendly reporting interface compared to Universal Analytics (UA). GA4 has been designed to make it easier for users to find and analyze the data they need.
In addition to a more user-friendly interface, GA4 also includes new features such as path analysis and funnels. Path analysis allows users to visualize the most common paths users take on their website or app, which can help identify opportunities for improvement. This was hard to do with Universal Analytics and typically required workarounds like this one. Funnels, on the other hand, provide a visual representation of the steps users take to complete a specific goal, such as making a purchase.
Overall, GA4 offers a more modern and powerful reporting interface compared to UA, with new features that can help businesses make better decisions based on their website or app data.
Conclusion
The forced migration to GA4 is coming this July and while UA is still more widely used, GA4 has several advantages, such as improved tracking code, more advanced data analysis, and streamlined e-commerce tracking. With its event-driven model, GA4 can track more complex user interactions, making it a valuable tool for businesses that want to gain deeper insights into their user behavior.
AUTHOR BIO:
The EasyAutoTagging staff is made up of seasoned pros in digital marketing, marketing analytics, and ad tech. They’ve brought a wealth of experience and hands-on knowledge to our blog and help documentation over the years. From in-depth articles on the latest industry trends to easy-to-follow guides. You can explore more of their articles here.
Leave a comment